
Isotretinoin: Safety Alert issued by Health Canada and DRAP-PRAEC
What is Isotretinoin?
Isotretinoin is a retinoid used orally for the treatment of severe, recalcitrant nodular acne that does not resolve after using conventional therapies such as systemic antibiotics.
Isotretinoin produces it effect via acting on cell cycle, cell differentiation, survival, and apoptosis. These actions decreases the sebum production, and inhibits the blockage of pores, and the growth of acne causing bacteria.
Usual Side Effects:
- Cheilitis (dry lips)
- Xerosis (dry skin)
- Xerostomia (dry mouth)
- Rhinitis sicca (dry nose)
- Photosensitivity.
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Rhabdomyolysis Back and joint pain
- Impaired hearing, including tinnitus, has been observed in patients receiving systemic isotretinoin.
Contraindications:
- Isotretinoin is contraindicated in pregnant women or those who are trying to get pregnant.
- Patients taking isotretinoin should avoid blood donation while on isotretinoin and for 1 month after the discontinuation of the treatment with isotretinoin. This is done to reduce the risk of embryo-fetal toxicity.
- Visual disturbances, including corneal opacities, nyctalopia, and xerophthalmia, should be observed while the patient is on isotretinoin.
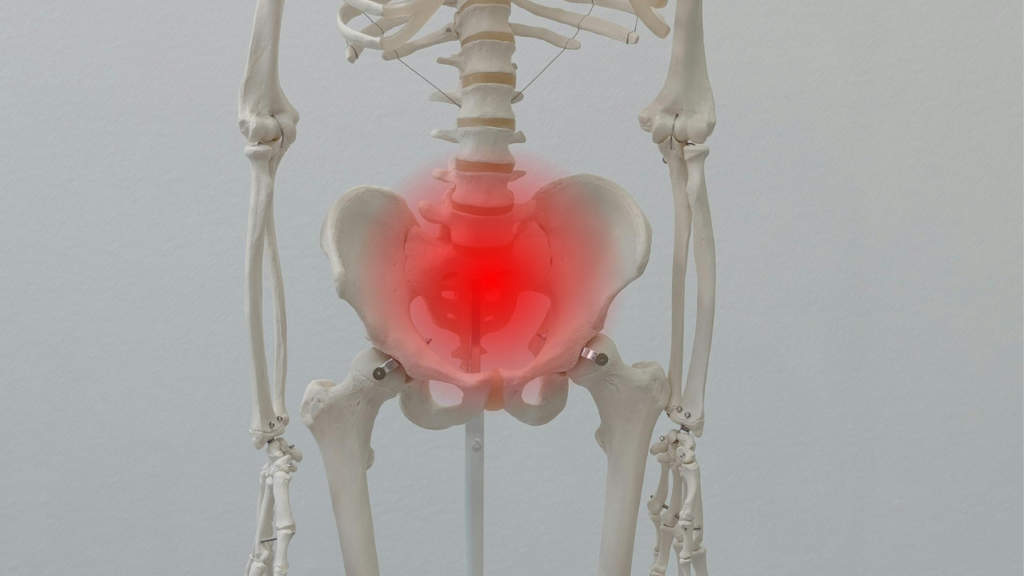
Apart from all these side effects, Health Canada and DRAP-PRAEC (Drug regulatory authority of Pakistan- Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Expert Committee) has instructed another adverse effect to be included in the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) of isotretinoin. That adverse effect of isotretinoin is sacroiliitis.
Sacroiliitis is the inflammation of the sacroiliac joint (SI), the joint which connects the ilium to the sacrum bone. The sacroiliac joint (SI) is one of the biggest joints in the body.
The association of isotretinoin with sacroiliitis was first assessed and communicated by health canada through Infowatch Newsletter (March 2025).
Health canada- Infowatch Newsletter (March 2025):
Health Canada, through its Infowatch Newsletter (March 2025), communicated the results of a safety assessment regarding the potential risk of sacroiliitis associated with isotretinoin use. The review identified a possible link between isotretinoin and sacroiliitis and indicated that Health Canada would collaborate with manufacturers to update the Canadian Product Monograph (CPM) to include this risk.
Sacroiliitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the sacroiliac joints, which connect the spine to the pelvis, and typically presents with pain.
Health Canada reviewed 24 international case reports of sacroiliitis in patients receiving isotretinoin. Of these, 23 cases were considered possibly related to isotretinoin use, while one case was deemed unlikely to be associated. The mean age of affected patients, where reported, was 20 years. No fatalities were reported.
Additionally, 18 scientific publications were evaluated. Although the studies supported an association between isotretinoin use and sacroiliitis, no definitive biological mechanism explaining this relationship was identified. In both case reports and published literature, symptoms of sacroiliitis improved following discontinuation of isotretinoin and appropriate medical management.
 DRAP-PRAEC Regulatory Action in Pakistan
DRAP-PRAEC Regulatory Action in Pakistan
This safety concern was discussed during the 6th meeting of the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Expert Committee (PRAEC) held on 31 December 2025. In accordance with Rule 10(1)(h)(iv) of the Pharmacovigilance Rules, 2022, the Committee decided that registration holders of isotretinoin-containing products must update the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) and product labeling to include information on the risk of sacroiliitis under the Adverse Drug Reactions and Warnings and Precautions sections, aligned with the Health Canada Product Monograph.

Advice for Healthcare Professionals and Patients
Healthcare professionals and patients are advised that isotretinoin use may be associated with sacroiliitis (inflammation of the pelvic joints). Patients should seek medical advice if they experience persistent lower back, hip, or buttock pain—particularly pain that worsens at night or during rest. Patients should not discontinue isotretinoin therapy without consulting their healthcare provider.
Reporting of Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)
Healthcare professionals and patients are encouraged to report any suspected adverse drug reactions associated with isotretinoin or any other medicines to the National Pharmacovigilance Centre (NPC), Drug Regulatory Authority of Pakistan (DRAP), through the Med Vigilance E-Reporting System (E-forms) available on the DRAP website. Reports may also be submitted via the VigiMobile application.
References:
DRAP Safety Alert (Government safety communication)
Drug Regulatory Authority of Pakistan. (2026, January 30). Safety alert of risk of sacroiliitis with isotretinoin. https://www.dra.gov.pk/safety_info/safety_communication/safety_updates/safety-alert-of-risk-of-sacroiliitis-with-isotretinoin/NCBI Bookshelf – Isotretinoin (StatPearls article)
Pile, H. D., & Patel, P. (2025). Isotretinoin. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525949/DrugBank Entry – Isotretinoin
Wishart, D. S., Feunang, Y. D., Guo, A. C., Lo, E. J., Marcu, A., Grant, J. R., & Wilson, M. (2026). Isotretinoin (DB00982). In DrugBank Online. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00982NCBI Bookshelf – Sacroiliitis
Sacroiliitis. (2024). In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448141/
Pharma Bulletin, Research Articles & Case Studies
Disclaimer
This content is shared solely for educational and public awareness purposes and is based on publicly available DRAP safety alert notices. It does not represent an official DRAP communication, medical advice, or regulatory directive. Readers consult qualified healthcare professionals before making any medical or regulatory decisions.











